
1C launches nation's largest EV charger marketplace, bringing chargers from renowned OEMs under a singlemplatform, offering convenience & options for EV owners.
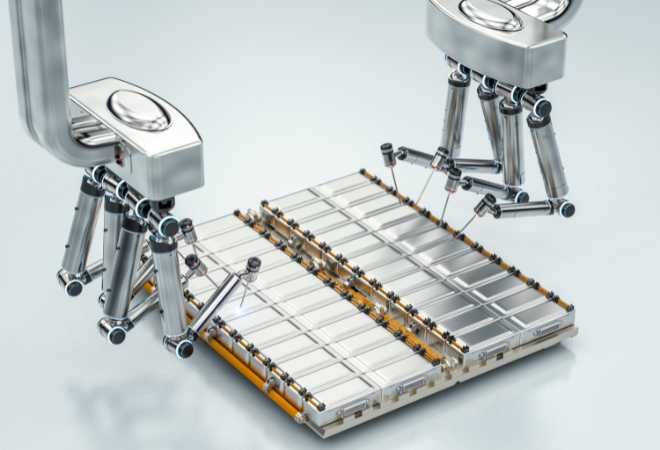
Battery swapping in electric vehicles (EVs) is a process where the depleted battery is replaced with a fully charged one, typically at specialised stations. Unlike traditional charging methods that take hours, battery swapping offers a swift solution, taking only about 5 minutes. This method enhances the convenience of EV usage, particularly for long journeys, as it significantly reduces downtime. Although the technology is not widespread in India, ongoing advancements may lead to increased adoption in the future. This approach addresses concerns related to charging times, making EVs more practical for users. In this context, discussions around the availability, legality, and cost aspects of battery swapping are crucial considerations for the country’s evolving landscape of electric mobility.
Swapping an electric vehicle battery means changing the battery to a fully charged one. This happens at a particular station or a service that comes to you.
The significant advantage of battery swapping is that it’s much faster than regular charging. Charging at a station can take up to 8 hours, but swapping a battery can take 5 minutes.
This makes battery swapping good for long trips. It cuts down the time an EV is not on the road. Also, it lets EVs be used more often and for longer times, as there’s no waiting for the battery to charge.
There are few battery swapping stations, but that might change as the technology becomes more common.
Different battery swapping systems come with pros and cons. The common one is automated, using robots for fast swaps but costly setups. Manual methods are cheaper but slower and need more human effort. Semi-automated combines features, offering speed between manual and automated, and is usually more budget-friendly. Regardless of the choice, battery swapping is an excellent alternative to charging stations.

Several companies offer battery swapping services in India, but not all are nationwide. Some notable ones include Ola Electric, Amara Raja, Amplify Mobility, Esmito Solutions, Gogoro, ChargeMYGaadi, EChargeUp Solutions, Lithion Power, NIO, Numocity, Oyika Pte, Panasonic India, Revolt Motors, SUN Mobility, TATA Power, Okaya, and BatterySmart.
Gogoro is a Taiwanese company specialising in battery swaps for electric two-wheelers. In Taiwan, 95% of electric two-wheelers use Gogoro’s solution. The company has now entered the Indian market by partnering with Hero Motocorp.
There are two main types of EV Battery Swapping.
In this model, EV battery services are treated as a subscription, akin to services like PNG. Here, the rates for swapping batteries are generally lower than one would pay under the pay-per-use model.

Under this model, drivers pay based on their actual usage, as there is no fixed driving pattern. For instance, drivers with shorter commutes that don’t require frequent battery swaps are more likely to opt for the pay-per-use model.
Pure Electric Vehicles run solely on electric batteries, also known as Battery Electric Vehicles. The battery undergoes discharge cycles during driving and charges when plugged in, affecting its capacity over time.
The battery pack constitutes 40%-50% of an electric vehicle’s cost, significantly influencing the price difference between EVs and traditional vehicles. This cost impact persists at the time of purchase and in subsequent years.
Replacement is often covered if within the warranty period ( 8 years and 100,000 miles). However, once out of warranty, replacement costs are borne by the owner.
A 1 kWh lithium-ion battery pack costs around Rs 18,000-22,000. But this cost can vary from company to company and model to EV. For instance, if you need to replace the battery pack for a Tata Nexon EV (31 kWh), it would be around Rs 5.50-6.20 lakh. Similarly, for an MG ZS EV (44.5 kWh), the replacement cost would be about Rs 6.60-8.50 lakh.
McKinsey reports an 80% decrease in battery prices from $1000 to $227/kWh between 2010 and 2016. The continuous decline suggests that future replacement costs will differ significantly from today.
EV batteries are proven to last many years, backed by warranties ranging from five to eight years. Nissan offers an 8-year warranty, while M.G. Motors provides a 7-year warranty globally.
Research indicates a 16% decline in battery pack cost from 2007 to 2019, estimating the average price to be $161/kWh 2019. Following this trend, a 100 kWh battery’s out-of-warranty replacement cost in 2025 could be $5,600.
Electric vehicle (EV) battery swapping presents a swift and practical solution, particularly for long journeys, addressing concerns related to traditional charging times. While ongoing advancements in India may lead to increased adoption, discussions surrounding availability, legality, and cost aspects remain pivotal. The varied models, such as Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) and Pay-Per-Use, offer flexibility to users. Despite potential challenges, EV battery swapping holds promise with benefits like faster charging, alleviating range concerns, and enhanced battery inspection. The cost of replacing EV batteries in India, influenced significantly by the battery pack, reflects a dynamic landscape influenced by ongoing developments, cost trends, and policy considerations.
Answer: The availability of battery swapping in India is still being determined, with ongoing challenges in formulating a comprehensive policy. Discussions are underway, and Minister Nitin Gadkari’s recent response suggests ongoing negotiations.
Answer: The legal status of EV battery swapping in India is questioned as policy formulation faces hurdles. Minister Gadkari’s parliamentary response indicates ongoing discussions, leaving the situation uncertain.
Answer: Battery swapping in electric vehicles involves exchanging a depleted battery with a fully charged one at specialised stations. This quick process reduces downtime, benefits long trips, and improves overall EV usage.
Answer: Different types include automated (fast but costly), manual (cheaper but slower), and semi-automated (a balance between speed and affordability). Regardless of the type, battery swapping is a valuable alternative to traditional charging.
Answer: A 1 kWh lithium-ion battery pack costs around Rs 18,000-22,000. If you need to replace the battery for a Tata Nexon EV (31 kWh), it could be around Rs 5.50-6.20 lakh. For an MG ZS EV (44.5 kWh), the replacement cost might be between Rs 6.60 and 8.50 lakh.
1C launches nation's largest EV charger marketplace, bringing chargers from renowned OEMs under a singlemplatform, offering convenience & options for EV owners.
Explore the surprisingly long history of electric vehicles. Start from 1830s with dawn of EVs, go through 1900s when electric cars dominated the roads, move through the 60s, when ICE rose to popularity, and cruise through the 21st century to understand the rebirth of electric vehicle in automobile industry.
Can you charge your EV to 80% in 10 minutes? Discover the truth about fast charging and how 1C helps you find verified stations. Stay informed & charge wisely!
Amidst EV evolution, the 1C app has emerged as a gamechanger, setting new standards in the market. But what makes it stand out in an increasingly crowded space?
1C EV Charging App can help EV owners in Delhi-NCR in planning road trips. It eliminates the uncertainty of long drives with EV, ensuring a smooth journey.
1C EV Charging App has taken a proactive approach to ensure that EV owners can access 100% verified charging stations whenever and wherever they need them.






© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved