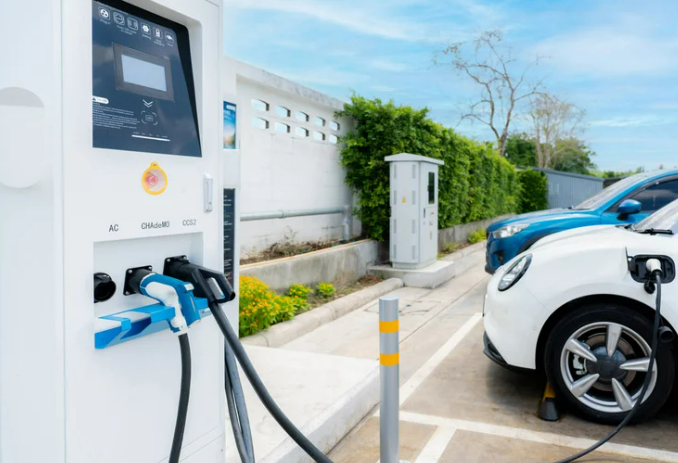
How Do EV Charging Stations Get Their Power?
Electric car charging stations receive power from two main sources: the electricity grid and off-grid solar energy. Most stations depend on grid electricity, which offers a consistent and dependable power source. This electricity is usually sourced from the same grid supplying homes and businesses.
In contrast, solar-powered stations operate using their own off-grid electricity system. These systems use solar panels to collect and store energy from the sun, which is then used for charging electric cars. While solar-powered stations entail higher setup costs, they are environmentally friendlier as they do not depend on grid-based power.

Where Do EV Charging Stations Get Power?
Electric car charging stations get their power from the electrical grid, where various methods generate electricity. In the United States, the primary sources include coal, natural gas, and nuclear power, with a growing contribution from renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower due to technological advancements.
Some charging stations specifically use solar or wind power, earning the labels of solar-powered or wind-powered charging stations. These stations employ solar panels or wind turbines to generate electricity, storing it in batteries for later use. As battery technology advances, charging stations with batteries are becoming more prevalent, offering continuous electric charging accessibility, irrespective of the location.
Advantages of Electric Car Charging Stations:
- Convenience: Electric vehicle owners can charge their cars during their daily activities.
- Cost-Effective: EV owners can save money on fuel and maintenance costs in the long run.
- Environmentally Friendly: Charging stations using clean energy contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Affordable: As EV adoption increases, the cost of EV charging stations is gradually decreasing.

Energy Sources for Electric Car Charging Stations
Electric car charging stations derive energy from various sources, including:
Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar: Generated from the sun through photovoltaic panels, converting sunlight into electricity. Stations using solar energy can function independently of the power grid, reducing electricity expenses.
- Wind: Produced by turbines powered by wind, similarly operating independently of the grid, thereby cutting down on electricity costs.
Non-renewable Energy Sources
Despite the growing emphasis on renewable sources, a notable portion of electric car charging stations still relies on non-renewable energy. Examples include:
- Coal: Contributes to thirty-eight percent of electricity generation in the US. While economical, coal is less environmentally friendly than renewable alternatives.
- Oil Reserves (Petroleum): Although its global usage is declining, petroleum remains significant for electricity generation and transportation fuel.
- Natural Gas: Generates fewer carbon emissions compared to coal and oil, making it a cleaner option. A substantial portion of US energy production stems from natural gas.
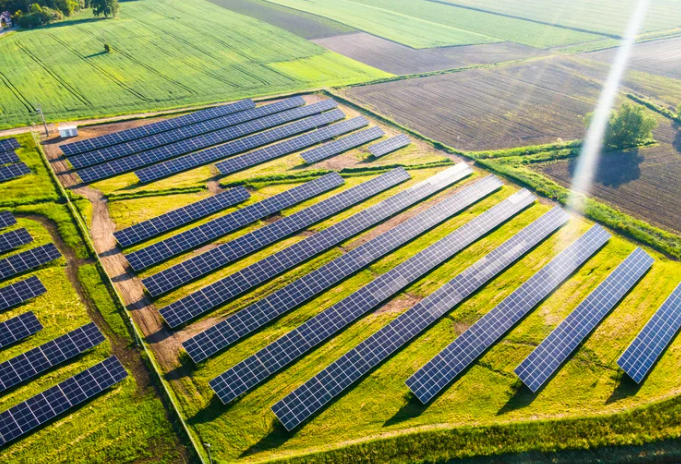

How Renewable Sources Power Electric Cars?
Electric cars have gained popularity in recent years due to increased awareness of the environmental impact of carbon emissions. The charging process of these cars also contributes significantly to reducing carbon emissions. In this section, we’ll examine the environmentally friendly aspects of charging stations and how renewable sources facilitate the powering of electric cars.
Electric cars function using electricity stored in their batteries. Charging an electric car resembles charging a phone but on a larger scale. However, electric cars require a considerable amount of power to operate, necessitating specialised charging stations for on-the-go charging.
Solar Energy: Solar-powered charging stations use energy from the sun to charge electric cars. These stations have panels that soak up solar energy and turn it into electricity. Some advantages of solar charging stations are:
- Solar energy is abundant and doesn’t cost anything.
- They don’t need fuel, so running them is cheaper.
- They’re easy to maintain because their design is simple.
Wind Energy: Wind-powered charging stations also exist. They use turbines to make electricity from the wind. These stations are connected to the electric grid, so the energy they produce can be sent to charging stations. Here are some benefits of wind-powered charging stations:
- Wind energy is plentiful and doesn’t cost anything.
- They don’t need fuel, so they’re cheaper to run.
- They’re easy to maintain because their design is simple.


Power Processes of Electric Car Charging Stations
Electric car charging stations work differently from traditional fueling stations. Here’s a simple explanation of how they power up electric cars:
- Power Conversion: The charging station takes electricity from the grid, which comes in alternating current form, and converts it into direct current (DC) power that can charge the car’s battery.
- Battery Management: The charging station talks to the car’s battery management system to keep things safe. It makes sure the battery doesn’t get too full or too hot, which could cause problems.
- Charging: Once everything’s set up and safe, the charging process starts. Electricity flows from the charging station into the car’s battery, filling it up.
4. Post-Charging Management: When the battery is full, the charging station stops sending electricity. This helps the battery last longer and prevents damage from overcharging.