Menu
Menu
Updated on Jun 11, 2023 | 3 min read
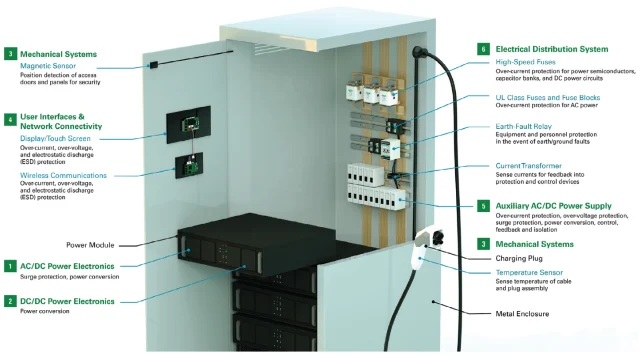
Charging stations typically require an AC power supply, which needs to be converted to DC for the electronic circuits to operate. The choice of AC to DC converter depends on several factors, including input voltage range, desired output voltage and current, efficiency, space, and cost. While older converters were less efficient and larger, advances in the electronics industry have led to smaller, more efficient models. Additionally, charging stations may require a DC-DC converter to facilitate power conversion at different levels.
To accurately calculate the cost of a charging session, the power consumption needs to be measured precisely. This is achieved through a subsystem that includes sensors and an integrated circuit to measure the voltage and current, allowing for accurate power consumption readings.
Users can locate the nearest charging station using mobile applications, and communication between the mobile interface and the charger is facilitated by IoT. The controller in each charging station allows for control of features, data transfer, and data storage.
Safety is a crucial consideration when designing a charging station, as incidents can pose risks to users and their vehicles. The safety subsystem employs miniature circuit breakers, fuses, surge protectors, and residual current detectors to prevent such risks.

Content Writer
© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved