
1C launches nation's largest EV charger marketplace, bringing chargers from renowned OEMs under a singlemplatform, offering convenience & options for EV owners.

Electric vehicles started becoming available in India around the early 2000s, but the significant progress in adopting and promoting electric vehicles in India started gaining momentum around the mid-2010s. The Indian government launched the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) India scheme in 2015. It provided financial incentives for electric and hybrid vehicles and supported the development of charging infrastructure, subsidies, and tax benefits for both manufacturers and consumers. These measures aimed to make EVs more attractive and affordable. Indian automotive companies collaborated with international partners to bring advanced electric vehicle technologies to the Indian market. Policies were formulated to encourage research and development in the field of electric vehicle technology.
But are these efforts enough to smoothen the use of EVs on Indian roads? In my view, it takes time and consistent development to make a new habit overtake an old one.
The widespread acceptance of electric vehicles within the populace, it demands a proper setup of charging infrastructure, diverse models for EV selection, price range, availability of policies, and a skilled workforce within the industry.
With the government, Indian EV manufacturers, market players, and international parties also invested in Indian Electric vehicle development.
1. Subsidies for electric vehicles increased to promote their adoption. Two-wheelers get up to Rs 15,000 subsidy per kWh of battery capacity or 40% of total cost, and three-wheelers/passenger vehicles can receive Rs 10,000 subsidy per kWh.
2. Investment of 35,000 crores for energy transition, benefiting stakeholders like NTPC, JSW Steel, and Tata Steel.

3. Reduced customs duty (13%) on Lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles and excise duty exemption on natural gas and biogas.
4. Significant investment of Rs. 19,700 crores in hydrogen fuel for cleaner energy sources.
5. Tax exemptions on Lithium-ion batteries and raw materials to promote green mobility.
6. Expectations from industry leaders include extending FAME II subsidies, reducing GST rates (from 18% to 5%) on lithium-ion batteries and cells, extending PLI scheme benefits, and relaxing FDI norms to boost investment and demand for EVs.
1. About 10,000 fuel stations in India offer EV charging, with Indian Oil leading with over 6,300 outlets. Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum also provide charging services.
2. State-run oil companies like Indian Oil, HPCL, and BPCL plan to establish EV charging at 22,000 pumps, aiming for 40% of their target. BPCL has launched over 90 EV fast-charging highway corridors covering more than 30,000 km.
3. Private fuel retailers like Shell and Nayara Energy also contribute to EV charging infrastructure, offering additional services like cafes and car care to generate extra revenue.
4. An Australian financial institution named Macquarie, plans to establish a non-banking financial company (NBFC) in India to provide credit support for businesses operating electric vehicle fleets. They aim for a substantial $400 million investment in their comprehensive EV platform.
5. Tata Power EV Charging Solutions Limited and Indian Oil Corporation collaborate to set up over 500 fast and super-fast charging points in major cities and highways across India.
6. Servotech Power Systems Limited introduces two patents for fast charging of GB/T Bharat DC 001 vehicles, aiming to revolutionise EV charging with a cost-efficient system.

7. Gogoro, known for smart battery-swapping technology, introduces eco-friendly solutions in India. Gogoro is starting the Battery Swapping in Delhi and Goa and planning expansion to Mumbai and Pune by mid-2024.
8. Pune-based KPIT Technologies introduces sodium-ion battery technology to reduce the cost of EV batteries by approximately 25-30% compared to existing lithium-ion batteries.
Ten years ago, people didn’t think much about electric cars. They didn’t seem practical and weren’t expected to compete with regular petrol and diesel cars. But now, in 2023, electric vehicles have taken growth in India.
In recent years, more Indians are choosing electric cars. In March 2023, Vahan data shows that 82% more EVs were sold compared to last year – that’s a big increase. They sold 1,39,789 units in March 2023, up from 77,128 in March 2022. Overall, sales went up a lot – from 4,58,746 in 2022 to 11,80,597 in 2023.
Electric two-wheelers are the most popular, selling over 1 lakh monthly in the second half of 2023. Ola Electric, TVS Electric, and Ather Energy are the top three companies in this category.
Even though the government is giving less help (subsidies went down), people are still buying electric two-wheelers. In September 2023, 63,715 were sold – 2% more than the previous year. The four-wheeler market is also growing. In 2022, 41,675 electric cars were registered – that’s a big increase from the previous year. In 2023, sales grew by 41.5% compared to September 2022.
The top electric car brands are Tata Motors, MG Motor, and Mahindra, with Tata having a big 68.8% market share. Luxury cars are also going electric. BMW is leading here with a 48% market share. Their new iX1 electric SUV sold out in just 180 minutes on launch day.
Even though electric cars are still a small part of the total market, they are expected to grow to 13% by 2030. Big brands like Volkswagen, Kia, and Range Rover are getting ready to join the Indian electric car market by 2025.
It’s not just personal cars; electric three-wheelers are also becoming popular, especially for moving goods. In March 2023, there was a 90% increase in passenger electric three-wheeler sales, and the cargo segment grew by 83% compared to March 2022. In the financial year 2022-2023, 4,04,143 electric three-wheelers were sold, a big 118% increase from the previous year.
Source: Times of India
According to the vehicle registration data for 2020-2023, it is clear that purchases of Electric vehicles have increased over the years. Still, at the same time, the number of other vehicles like diesel and petrol has also increased. It is still a long road to reduce fuel consumption and shift to electric vehicles for the masses.
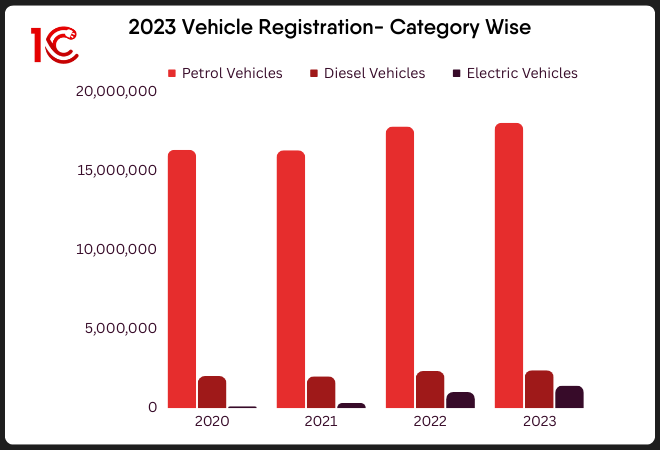
Source: Press Information Bureau
The India electric vehicle charging stations market is projected to witness robust growth, expecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 25% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2028. While the COVID-19 pandemic had a minor impact on the EV charging infrastructure market due to delayed manufacturing caused by supply chain disruptions, planned projects for new EV charging infrastructure by the public and private sectors remained largely unaffected. The Indian government, for instance, had outlined plans for approximately 69,000 EV charging stations in 2020.
The anticipated positive growth in India’s EV charging station market is attributed to the increasing demand for electric vehicles in the country. The expansion is also driven by the necessity for EV charging infrastructure in sparsely populated areas. However, challenges arise from the current low utilisation rates of EV charging stations in various regions, potentially hindering market growth.
Prevalence of Slow Chargers:
Technological Advancements:
Government Initiatives:
Source: Modor Intelligence
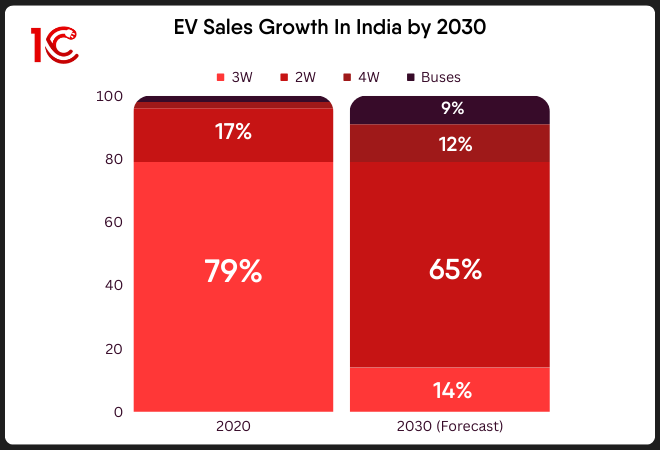
Source: NITI Ayog
Electric vehicles (EVs) in India come with lots of advantages, but there are also a few challenges to overcome for India to lead in the electric vehicle industry. Here are some key things:

One big challenge is the limited charging stations for EVs in India. It’s not always easy for EV owners to find a place to charge their vehicles right now. But the government and private companies are working to fix this. Some companies, like 1charging, have even launched affordable charging solutions for EV Fleet owners, on demand charger facilities for residential EV charging.
Check: 1C EV Battery Charger for Bike & Cars
The degree of awareness and perception among consumers plays a crucial role in shaping EV adoption. Many individuals still need to learn about the advantages and capabilities of electric vehicles, harbouring concerns regarding range, reliability, and charging time. To address this, both the government and automakers are proactively involved in awareness campaigns to educate consumers, debunking common myths and misconceptions.

Despite the rapid growth of the EV market in India, it remains in its early stages. Leading automakers such as Tata Motors, Mahindra, and Hyundai have introduced electric vehicle models, with more anticipated to follow. The government is promoting local manufacturing to reduce costs and enhance the accessibility of EVs.
Advancements in battery technology play a pivotal role in driving EV adoption. Enhancements in performance, range, and cost reduction are directly linked to innovations in battery technology. India is actively supporting local battery manufacturing, intending to further reduce EV costs, making them more competitive against traditional gasoline vehicles.

Beyond the challenges, EVs in India bring significant environmental and economic advantages. They emit fewer pollutants, contributing to the reduction of air pollution and the fight against climate change. Additionally, the operational costs of EVs are lower, making them a more economically viable option compared to traditional vehicles powered by gasoline.
While electric vehicles offer numerous benefits, there are several challenges hindering their widespread adoption in India. These include the high cost of vehicles, limited charging infrastructure, constrained range, restricted battery technology, and a lack of consumer awareness.
Also Read:
India is progressing towards the adoption of electric vehicles with the support of government regulations and evolving market dynamics. However, challenges are still there including inadequate charging infrastructure, high vehicle costs, and limited public awareness. The increasing popularity of electric bikes signals a shifting landscape. To ensure full readiness for electric cars by 2024, ongoing efforts are required to expand charging infrastructure, reduce vehicle costs, and enhance public awareness. While India has made noteworthy strides, still acknowledging these challenges is essential for the smooth integration of electric cars into the mainstream automotive sector.
1C launches nation's largest EV charger marketplace, bringing chargers from renowned OEMs under a singlemplatform, offering convenience & options for EV owners.
Explore the surprisingly long history of electric vehicles. Start from 1830s with dawn of EVs, go through 1900s when electric cars dominated the roads, move through the 60s, when ICE rose to popularity, and cruise through the 21st century to understand the rebirth of electric vehicle in automobile industry.
Can you charge your EV to 80% in 10 minutes? Discover the truth about fast charging and how 1C helps you find verified stations. Stay informed & charge wisely!
Amidst EV evolution, the 1C app has emerged as a gamechanger, setting new standards in the market. But what makes it stand out in an increasingly crowded space?
1C EV Charging App can help EV owners in Delhi-NCR in planning road trips. It eliminates the uncertainty of long drives with EV, ensuring a smooth journey.
1C EV Charging App has taken a proactive approach to ensure that EV owners can access 100% verified charging stations whenever and wherever they need them.
Streamline your EV charging with the 1C EV Charging App: 1 app, 250+ verified chargers, real-time data, and a user-friendly experience. Download now!
Right EV charger for your vehicle is important to ensure good performance. Navigate via various types, and key factors to consider when choosing an EV charger.






© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved