Menu
Menu
Updated on Jun 4, 2023 | 3 min read
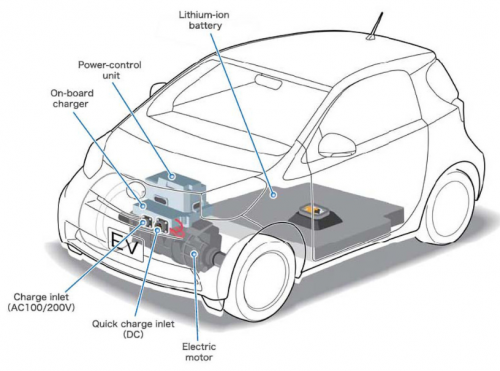
On-board chargers (OBC) are an important component of electric vehicles. They are often confused with charging stations, which are also called chargers. However, there are two types of chargers: the OBC, which is built into the car, and the charging station, which can be either AC or DC. There are two basic types of charging: direct current and alternating current. If AC power is used, the current passes through the charging cable to the OBC, which converts the AC current to DC and sends it to the battery. The OBC controls the current and voltage that the battery needs to be charged, thus taking care of the battery lifespan. It follows a strategy in which it is initially charged with a constant current, and when the voltage at both ends of the battery reaches a certain amplitude, it changes to constant voltage charging.
The OBC market is segmented based on power output, vehicle type, and propulsion type. Power output is studied under three categories: less than 10kW, 10 to 20kW, and more than 20kW. Propulsion type includes battery electric vehicle, hybrid electric vehicle, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. Vehicle type includes electric passenger cars, electric vans, electric buses, electric medium duty vehicles, electric heavy duty vehicles, electric agriculture tractors, electric construction equipment, and mining machines. The key players in the on-board charger market include Bell Power Solutions, Current Ways Inc, Toyota Industries Corp, AVID Tech Ltd, Infineon Technologies Ltd, and Xepics Italia SRL.
On-board chargers can be divided according to how many phases they can use and according to their output. The power output of on-board chargers is usually in the range of between 3.7 kW and 22 kW. These two characteristics determine the charger’s price and, therefore, the price of the whole electric car. Some companies, like AVID Technology Limited, use highly efficient on-board charger technology by using power switching and magnetics.

Content Writer
© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved