
CCS2, a versatile EV charging connector, integrates AC and DC systems for rapid charging. Common in Europe and India, it offers 50kW to 350kW power ratings.

Suppose your EV car is not just slowing down when you take your foot off the pedal but helping to charge itself. That’s where regenerative braking comes in for electric and hybrid vehicles. It’s like a short self-charging span that turns braking energy into power for your vehicle. Regenerative braking is a unique technique that is used in EVs to capture the energy that the vehicle has due to its motion.
Regenerative braking is a process used in some vehicles. When the driver applies the brakes, instead of slowing down, the system also captures and stores the energy usually lost as heat. This captured energy is then converted into electricity, which can be used to recharge the vehicle’s battery. Regenerative braking acts like recycling the energy that would otherwise go to waste during braking. This helps increase overall energy efficiency and extends the driving range of electric and hybrid vehicles. This happens because the electric motor in these cars can spin in two ways.
One way helps the electric vehicles move forward, and the other way turns the motor into a generator when you slow down. When you brake, part of the energy goes to the battery, and the rest helps the brakes stop the car. People sometimes call this “B mode.”
Kinetic energy is the energy that an object has when it’s moving. Cars have a lot of mass, so they have a lot of kinetic energy. When you brake in a regular car, the energy becomes heat, and most of it is lost. But in electric cars, they use it to power the battery.
So, when you take your foot off the brake, the car slows down, and the motor turns that slowdown into more power. The car may be stopping on its own. Some cars let you adjust how much regenerative braking happens. EVs show this on a gauge in the dashboard so you can see how much power you’re saving each time you stop.
All electric cars and hybrids use an energy called regenerative braking. Its efficiency depends on a few factors.
Firstly, if the car is new, it’s likely to have a better regenerative braking system. Some vehicles can save up to 70% of the energy usually lost when you brake.
How fast and how much you brake matters, too. If you often stop and drive in traffic, the system can save a lot of energy. But if you mostly drive on the highway without stopping much, saving energy is harder.
You can save more energy by slowing down from high speeds, like coasting down from 70mph. Some people have even recharged their cars by towing them, but it’s not a good idea to do it often.
To save the most energy, you need to brake at a certain speed. It might feel slower than braking in a regular car. If you do it right, you can add a bit more range to your car, especially when driving in the city. But it can’t fully recharge your car.
In regular cars that run on gas, braking makes a lot of energy go to waste.
With regenerative braking in electric cars, when you take your foot off the accelerator pedal, the electric flow from the battery to the motor stops. But, the spinning part of the motor (called the rotor) keeps spinning along with the moving wheels of the car.
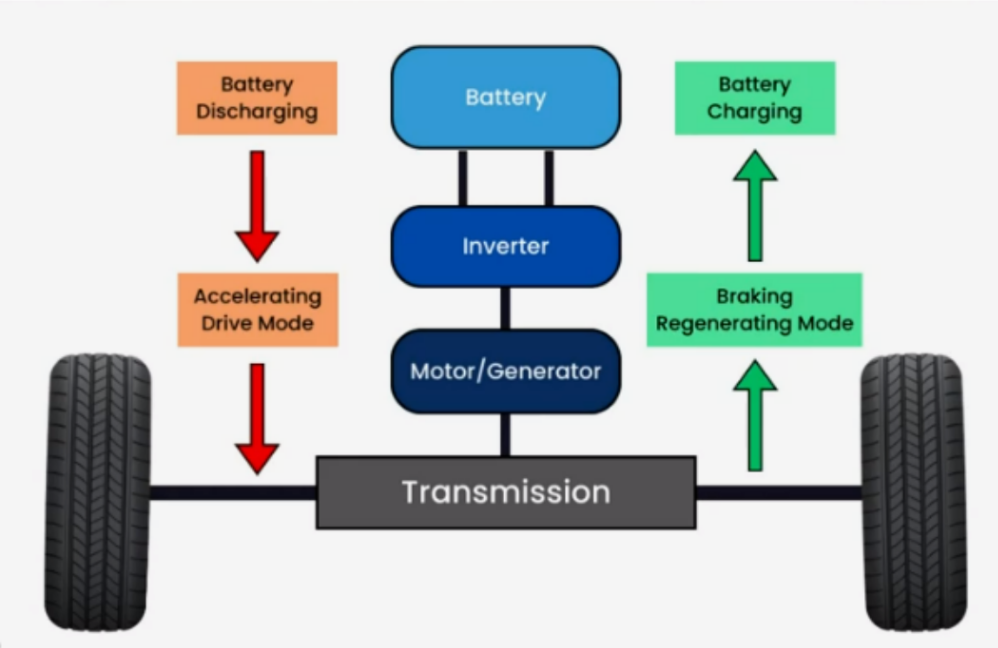
Since there’s no more electricity flowing from the battery, the motor becomes like a generator. It takes the energy from the spinning rotor and puts it back into the battery. At the same time, the rotor slowing down helps the car slow down, too.
Electric cars still have regular brakes, but they are like backups. They come into play if the motor has a problem if the car is going too slow for the generator to work well, or if the car needs to stop really quickly at very high speeds.
Electric cars use “torque blending” to find the right balance between regular brakes and regenerative braking. This smooths the braking, and most electric car drivers don’t notice the difference.
Regenerative braking is a smart way for electric and hybrid cars to save energy when braking. It helps these cars go farther on a single charge, making them more practical for everyday use. While it adds a smooth and enjoyable driving experience, it’s important to note that regenerative braking works best in certain conditions and has some limitations. Overall, it’s a beneficial technology embraced by major car companies for its efficiency and positive impact on electric vehicle performance.
CCS2, a versatile EV charging connector, integrates AC and DC systems for rapid charging. Common in Europe and India, it offers 50kW to 350kW power ratings.
Discover the 1C EV Charging App - your go-to solution for easily locating verified EV charging stations nearby. Simplify your journey today!
The EV Standardization has been the most significant missing part of the EV industry—standardisation in chargers, EV batteries, charging connectors, standard payment
MG ZS EV: Review Updated on May 30, 2023 | 4 min read [Sassy_Social_Share] The MG ZS EV has garnered attention in
Although Toyota is showing Zero interest in selling electric vehicles in India, it’s now going bullish on the US EV market. Toyota
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles show promise for sustainable transport in India. Challenges include infrastructure and cost, but the industry anticipates growth.
Will Tesla be affordable? Updated on Jun 21, 2023 | 5 min read [Sassy_Social_Share] The electric vehicle market in India has immense
Direct Current flows steadily in one direction, powering electronics, vehicles, and more. It's crucial for modern technology.






© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved