
Menu
Menu
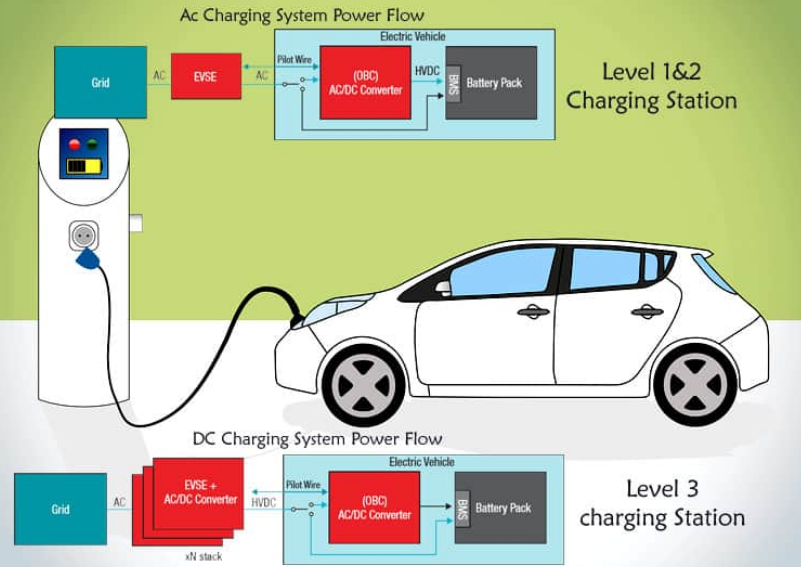
The onboard charger, which is also known as OBC, is a device designed to convert AC power from various sources into practical DC power. It is situated within the vehicle, and its primary function is power conversion. On board chargers offer the convenience of charging electric vehicles directly from home power outlets, eliminating the necessity for additional equipment for power conversion. This integration enhances user-friendliness and simplifies the charging process for electric vehicle owners.
Charging Station | Onboard Charger Type | Charging Methods Supported | AC Supply Specification | Power Rating | Time to Charge 24kW Battery Pack |
Home Charging | Integrated OBC | Constant Voltage, Constant Current | Standard Outlets | Up to 7kW | Approximately 3.5 – 4 hours |
Public Charging Station | Embedded OBC | Variable (Constant Voltage and Current) | Level 2 (240V, 30A) | 7-22kW | Approximately 1 – 4 hours |
Fast Charging Station | High-Power OBC | Constant Current | DC (480V, 100-350A) | 50-150kW | Approximately 1 hour |
Workplace Charging | In-Built OBC | Variable (Constant Voltage and Current) | Level 2 (240V, 30A) | 7-22kW | Approximately 1 – 4 hours |
DC Fast Charging | Rapid OBC | Constant Current | DC (480V, 100-350A) | Up to 350kW | Approximately 30 minutes |
The primary role of an on-board charger in electric vehicles is to regulate the flow of current from the grid to the traction battery that enables the charging from various sources and reduces dependency on dedicated charging stations. Moreover, the OBC controls the current and voltage levels during charging, which addresses two main charging methods: constant voltage and constant current. While constant current charging offers efficiency and speed, it may impact battery lifespan due to potential overcharging.
To mitigate this, a strategic approach is employed where the battery undergoes initial constant current charging and transitions to constant voltage charging after reaching a specific amplitude. This charging strategy underscores the crucial function of an EV onboard charger in optimising both charging efficiency and battery longevity.
The onboard charger in electric vehicles plays a crucial role in AC charging by converting alternating current from power sources, such as home outlets or public Level 2 charging stations, into direct current for the vehicle’s battery. It manages the flow of current, controls voltage levels, and ensures safe and efficient charging. The OBC’s integration enables electric vehicles to conveniently charge from standard AC power outlets, reducing the need for additional equipment and enhancing user accessibility.
In DC charging, the On-Board Charger remains inactive as it is not involved in direct current charging processes. DC fast charging stations provide direct current to the electric vehicle’s battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for rapid charging at higher power levels, significantly reducing charging time compared to AC charging. The OBC’s role in DC charging is minimal, emphasising the efficiency and speed provided by direct current fast charging technologies.
Following are some factors that need to be considered while designing an OBC.
The On-Board Charger is essential for easy electric vehicle charging, converting AC power to DC for use in regular outlets. This reduces the need for special charging stations. The OBC regulates current and voltage, making charging efficient and helping the battery last longer. Design factors like power rating, compatibility, efficiency, and safety are crucial for a reliable OBC. Manufacturers like BorgWarner, Hyundai Mobis, LG Electronics, Valeo, and Ficosa contribute to OBC advancements, enhancing electric vehicle accessibility and performance.






© 2024 Massive Mobility Private Limited. All rights Reserved